the core of our corporate values
PAD Stent Surgery Basic Info
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) refers to hardening or blockage of arteries in the lower extremities. PAD is often caused by atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries and can lead to leg pain, cramps, and difficulty walking. PAD occurs when the major arteries that supply blood to your limbs get narrowed or blocked.
Common Symptoms of PAD
Leg pain or achiness: Discomfort in the legs that occurs during activity or walking and goes away with rest. This is the most common symptom of PAD.
Intermittent claudication: Leg pain that forces you to stop walking, then disappears after resting.
Coldness in the legs: The legs feel cool to the touch due to reduced blood circulation.
Skin discoloration: Skin on the legs looks pale, bluish or reddish in color.
Slow wound healing or ulcers: Injuries or wounds on the legs are slow to heal due to lack of blood supply.
Painless muscle wasting: Muscle loss and weakness that you may not notice quickly.
If you experience one or more of these symptoms, you may likely have PAD. PAD can be diagnosed and localized with a physical exam, ultrasound, angiography or CT angiography. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can effectively relieve symptoms, prevent disease progression, and improve quality of life.
How To Treat Peripheral Artery Disease?
Treatment options for PAD include lifestyle changes, medications and procedures. Lifestyle changes such as exercise, diet, and smoking cessation can relieve symptoms and slow disease progression. Medications like statins and aspirin are often used to lower cholesterol and prevent clots.
When lifestyle changes and drugs are not enough, procedures may be needed to open or bypass blocked arteries. The main procedures are:
Angioplasty - A minimally invasive procedure where a balloon catheter is used to open the blocked artery. Stents are often placed to help keep the artery open. This relieves symptoms quickly.
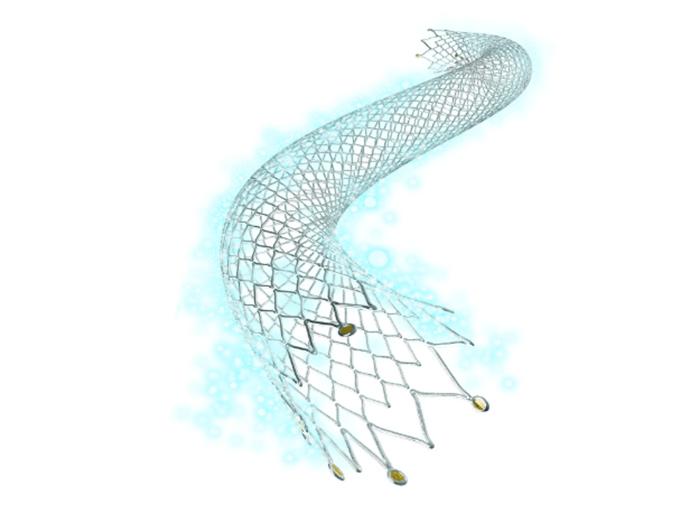
Stents - Placed in arteries during angioplasty to permanently hold them open.
Atherectomy - Uses a catheter to shave away artery plaque, allowing better blood flow.
Bypass surgery - Veins or arteries from elsewhere in the body are used to reroute blood around blockages. For severe blockages when other treatments won't work.
PAD stent placement, or leg angioplasty with stents, greatly improves circulation, mobility and quality of life. Success rates are high, though re-narrowing is possible. Close follow-up and lifestyle changes help maximize benefits.
PAD Stent Procedure
PAD stent placement is a minimally invasive treatment to open blocked arteries and improve blood flow in the legs. The procedure involves inserting a catheter into the artery, inflating a balloon to open the blockage, and placing a peripheral artery disease stent to keep the artery open. The procedure is typically done under local anaesthesia. It takes 1 to 2 hours and only requires a small incision. Patients usually stay in the hospital overnight before returning home. The key steps are:
1. Make an incision, often in the groin, to reach the blocked artery.
2. Thread a catheter through the artery to the blockage using X-ray guidance.
3. Inflate the balloon to open the blockage.
4. Place peripheral artery disease stent to support the artery walls. Additional stents may be needed for severe blockages.
5. Remove the catheter and close the incision. Recovery involves mild discomfort at the incision site which improves with medication and activity. Walking and light exercise aid healing and circulation. Follow-up care monitors artery health and risk factors like smoking or diet that contribute to re-narrowing.
PAD Stent Surgery Recovery
After PAD stent surgery:
Walk and do light activity as tolerated. Avoid prolonged standing/sitting. Elevate legs when resting.
Take all medications as prescribed to prevent clots and support stent. This typically includes aspirin and drugs for blood pressure/cholesterol.
Quit smoking. Continuing to smoke reduces stent effectiveness.
Get regular follow-up to monitor your stent.
Expect some incision discomfort for days/weeks.
Return to normal activities in 4 to 6 weeks. Avoid heavy exercise and lifting for several weeks.
Eat a healthy diet low in sodium, fat and cholesterol.
Return