the core of our corporate values
How is Coil Embolization Performed?
Blood vessel therapy is a minimally invasive method for diagnosing and treating patients from within blood vessels. In the case of cerebral aneurysms, this treatment is called coil embolization or "coiling".
Coiling does not require open surgery. Instead, doctors use real-time X-ray technology called fluoroscopy to visualize the patient's vascular system and treat diseases from within the blood vessels.
Minimally invasive coil embolization
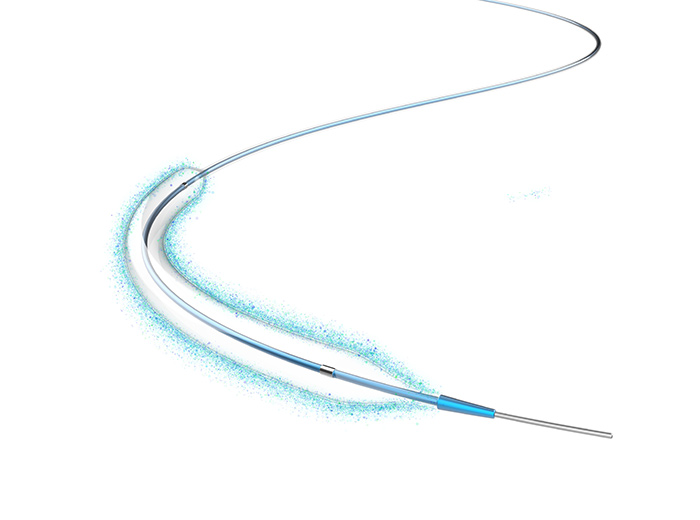
Embolization involves inserting a catheter through the patient's femoral artery in the leg and threading it through the vascular system into the patient's head and to the aneurysm. The entire process is accomplished using continuous X-ray visualization and high-speed radiographic techniques.
Once the doctor detects the presence, size, and location of the aneurysm, a smaller "microcatheter" is then placed inside the initial catheter. When the microcatheter successfully enters the opening of the aneurysm, the coiling system is introduced.
Platinum coils are deposited within the aneurysm, reducing or blocking blood flow to the aneurysm. Coils are made of platinum, so they can be seen through X-rays, and are flexible enough to conform to the shape of the aneurysm. The purpose of coiling is to tightly wrap around the aneurysm to prevent blood flow to the aneurysm and prevent it from rupturing.
Once placed inside the aneurysm, there is a small electric current passing through the wire. Due to this electrolytic action, the coils separate from the wire and remain inside the aneurysm.
After the aneurysm is filled, the catheter is removed and the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit for monitoring and further care.
The coiling procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Postoperative development of coil embolization
Patient undergoing coiling surgery before the aneurysm ruptures can expect to spend the night in the intensive care unit for monitoring. Typically, they will not experience pain or scarring due to coiling surgery.
Patients with ruptured aneurysms tend to stay longer in the intensive care unit, usually 10-14 days.
Experience is important when time is of the essence. When a patient is diagnosed with a cerebral aneurysm, time is of the essence. There is a 50% mortality and morbidity rate after the first rupture of an aneurysm, which increases to 75% after the second rupture.
Comparative studies of endovascular coil embolization and surgical treatment for unruptured cerebral aneurysms found that endovascular embolization was associated with shorter hospitalization and recovery time.
In addition, studies show that for patients who are equally suitable for open surgery and spring coil embolization, endovascular spring coil embolization treatment results in better patient outcomes with no disability within one year than surgery.
The relative risk of death or severe disability one year after coil treatment was 22.6% lower among patients who received coiling treatment than among those who had surgery.*